Horizontal Blocks in Contact
Horizontal blocks in contact is a classic problem that considers both Newton’s 2nd and 3rd laws. Consider two objects A and B, with masses of 5kg and 3kg respectively, that are being pushed with a force of 40N to the right as shown below:
Newtons 3rd Law predicts that A exerts a force on B and B exerts an equal but opposite force on A:
![]()
We can consider a few aspects of this problem:
If the total force acting on both objects is 40N and they have a combined mass of 8kg, according to Newton’s 2nd law the acceleration of both objects:
![]()
![]()
![]()
We can now determine the net force acting on each object:
Object A: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Object B: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Based on Newtons 3rd we can see that the reaction force of B on A; ![]()
We can now observe the net force acting on A, ![]() which agrees with our working above.
which agrees with our working above.
Solving these problems requires an understanding of the forces analysed above.
Example 1:
In the diagram below, box A has a mass of 8kg and box B has a mass of 5kg. A force of 78N acts on the boxes to the right. Calculate the following:
a) the acceleration of the boxes
b) the force acting on box A and B
c) the reaction force of B on A
a) Using Newtons 2nd law: ![]()
![]()
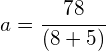
![]()
b) Again, using ![]() and the answer to part a:
and the answer to part a:
Box A: ![]()
![]()
![]() right
right
Box B: ![]()
![]()
![]() right
right
c) The reaction force of B on A is equal and opposite to the force of A on B:
![]() left
left
